An Instrumentation amplifier is a kind of differential amplifier with additional input buffer stages. The addition of input buffer stages makes it easy to match (impedance matching) the amplifier with the preceding stage. In other words, we can say that the differential op-amp circuit providing high input impedances with ease of gain adjustment through the variation of a single resistor is called the Instrumentation amplifier.
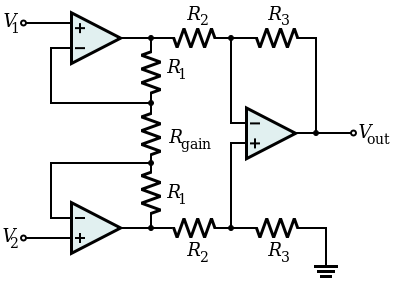
The gain of the Instrumentation Amplifier circuit is given by
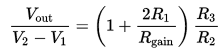
Note: An instrumentation amplifier can also be built with two op-amps to save on cost, but the gain must be higher than two (+6 dB).
Advantages of Instrumentation amplifier
The main advantages of using Instrumentation amplifiers are
- It has very low DC offset.
- There is low drift.
- It has low noise.
- It has a very high open-loop gain.
- It has very high common-mode rejection ratio(CMRR).
- It has very high input impedances.
Applications of Instrumentation amplifier
Instrumentation amplifiers find applications in measurement, industrial automation, biomedical engineering, etc.
- It is used along with sensors and transducers for measuring and extracting very weak signals from noisy environments.
- These amplifiers are used in biomedical sensors such as blood pressure sensors, ultrasound transducers, etc. that require very high impedance.
- It is used in High-frequency signal amplification in cable RF systems.
- It is used in Audio applications involving low amplitude audio signals in noisy environments to improve the signal to noise ratio.
- It is used in Navigation, and Radar instrumentation.
- It is used in High-speed signal conditioning for video data acquisition and imaging.
Where the Instrumentation amplifiers are used?
Instrumentation amplifiers are used where great accuracy and stability of the circuit both short and long-term are required.
