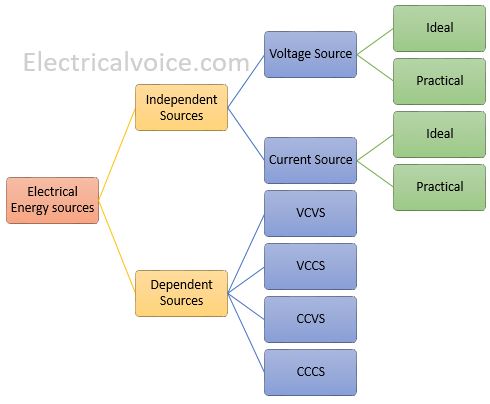
Classification of Electrical Energy Sources
Electrical energy sources are majorly classified into two classes i.e. Independent sources and Dependent sources. The independent sources are further divided into two types namely voltage source and the current source. There are four types of the dependent sources. They are as follows 1. Voltage Controlled Voltage Source (VCVS) 2. Voltage Controlled Current Source (VCCS) 3. … Read more