Servomechanism
It is a feedback control system in which a controlled variable or the output is a mechanical position or its time derivatives like velocity and acceleration.
Servomotors have two main classifications based on servomechanism i.e.
1. DC Servomotors
- Armature controlled DC motor
- Field Controlled DC motor
2. AC Servomotors
1. DC Servomotors
DC ServoMotor essentially an ordinary DC motor except for some minor difference and constructional features. For servo applications, a DC motor is required to produce Rapid acceleration from standstill. Therefore, a physical requirement of such a motor or low inertia and high starting torque. Low inertia is attained by reducing armature diameter with the corresponding increase in armature length.
a). Armature controlled DC motor
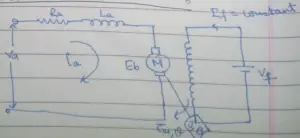
where
Ra = armature resistance
La = inductance of armature winding
Va = applied armature winding
Ia = armature current
Eb = back emf
J = Moment of inertia acting on motor shaft
B = viscous friction acting on motor shaft
Tm = Torque developed by the motor
θ = Angular displacement i.e. output


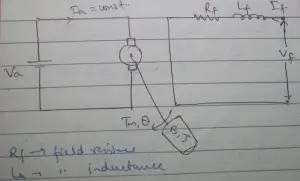
b). Field Controlled DC Motor