Microprocessor Definition
A microprocessor is a multi-purpose, Programmable, clock driven, register-based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device called memory, accepts binary data as input and processes data according to those instructions and provide results as output.
OR
It is an electronic device that fetches instructions from memory, execute them and provide results. A microprocessor is an electronic device that has computing and decision-making capability.
Nowadays many communication, digital entertainment, portable devices, are controlled by them.
Instructions
Each microprocessor is designed to execute a specific group of operations. This group of operations is called an instruction set. This instruction set defines what the microprocessor can and cannot do.
Note: A microprocessor cannot perform any task on its own.
The microprocessor can be embedded in a larger system and can function as the CPU of the computer called a microcomputer. A microcomputer consists of microprocessor, memory, input device and output device.
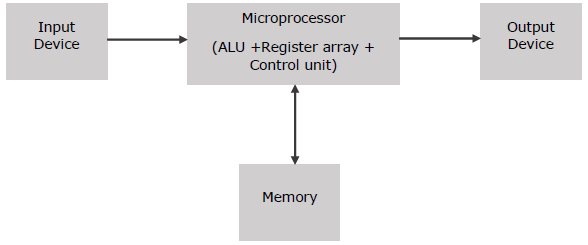
Microcontroller
A microcontroller is a programmable device that includes microprocessor, memory and I/O signal lines on a single chip, fabricated using VLSI technology. Microcontrollers are also known as single microcomputers.
- The microprocessor can be programmed to perform functions on specified/given data by writing specific instructions into its memory.
- The microprocessor reads one instruction at a time, matches it with its instruction set, and performs the data manipulation specified.
- The result is either stored back into memory or displayed on an output device.
Basic Units of a Microprocessor
The basic units or blocks of a microprocessor are
- ALU (Arithmetic & Logic Unit)
- An array of registers
- Control unit
Software
The Software is a set of instructions or commands needed for performing a specific task by a programmable device or a computing machine.
Hardware
The Hardware refers to the components or devices used to form computing machine in which the software can be run and tested. Without software, the Hardware is an idle machine.
Program
A program is a sequence of instructions that bring data into the microprocessor, processes it and sends it out.
Applications of Microprocessors
Some of the applications are:
1) Analytical scientific instruments
2) Smart terminals
3) Stacker crane controls
4) Conveyor controls
5) Word processor
6) Point of scale systems
7) Standalone electronics cash system
8) Electronic games
9) Vending and dispensing machines
10) Market scales
11) Traffic light controls
12) Home heating and lighting controls
13) Security & fire alarm system
14) Home appliances
15) Computer-aided instruction
16) Online control of lab instrumentation
17) Desktop computers
18) Check processor
19) Payroll system
20) Inventory control
21) Automatic type setting
22) Compact business machines
23) Medical instrumentation
24) Automobile diagnostics
25) Data communication processing
26) Optical character recognition
27) I/O terminal for computers.
