In this article, we will discuss the Difference between 8085 and 8086 Microprocessor.
| 8085 Microprocessor | 8086 Microprocessor | |
| Size | 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor. | 16-bit microprocessor |
| Address Bus | 8085 has 16-bit address bus | 8086 has 20-bit address bus |
| Memory | 8085 can access upto 216 = 64 Kb of memory. | 8086 can access upto 220 = 1 MB of memory. |
| Instruction Queue | 8085 doesn’t have an instruction queue. | 8086 has instruction queue. |
| Pipelining | 8085 does not support pipelined architecture. | 8086 supports pipelined architecture. |
| Multiprocessing Support | 8085 does not support multiprocessing support. | 8086 support multiprocessing support |
| I/O | 8085 can address 28 = 256 I/O’s | 8086 can access 216 = 65,536 I/O’s |
| Arithmetic Support | 8085 only supports integer and decimal. | 8086 supports integer, decimal and ASCII arithmetic. |
| Multiplication and Division | 8085 doesn’t support. | 8086 supports. |
| Operating Modes | 8085 supports only single operating mode. | 8086 operates in two modes. |
| External Hardware | 8085 requires less external hardware. | 8086 requires more external hardware. |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Memory Segmentation | memory space is not segmented | memory space is segmented |
Comparison of 8085 and 8086 Microprocessor
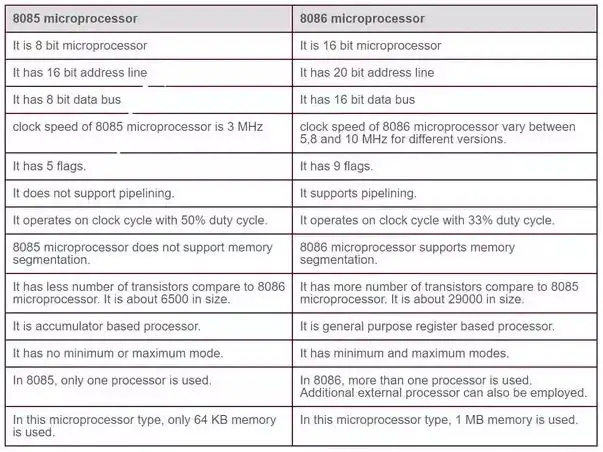
8085 Microprocessor
- 8085 is 8-bit Microprocessor.
- 8085 has 16-bit address line.
- 8085 has 8-bit data bus.
- The speed is 3 MHz.
- 8085 has 5 flags.
- It does not support pipelining.
- It does not support memory segmentation.
- 8085 has 6500 transistors.
- 8085 has no minimum or maximum mode.
- 8085 only 64 KB memory is used together.
8086 Microprocessor
- 8086 is 16-Bit Microprocessor.
- 8086 has 20-bit address line.
- It has 16-bit data bus.
- The speed can vary between 5,8, and 10MHz for three different microprocessors.
- 8086 has 9 flags.
- It supports pipelining.
- It supports memory segmentation.
- 8086 has 29000 transistors.
- 8086 has a minimum or maximum mode.
- 1 MB memory is used.
The comparison table is shown below.