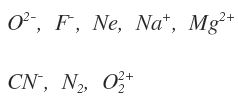Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers.
Atom
The smallest particle of an element is called an atom. An atom can take part in chemical combination and does not occur free in nature. The atom of the hydrogen is the smallest and lightest. Example- K, Na, H, He, Si, etc.
Molecule
A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or compound that can have a stable and independent existence. Example- O2, N2, Cl2, P4, S8, etc.
Atomic Mass
The atomic mass of an element is a number which states that how many times the mass of one atom of an element is heavier than 1/12th mass of one atom of carbon-12.
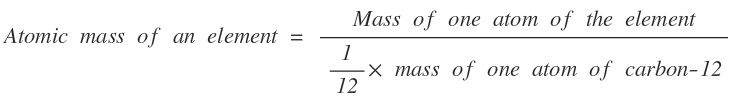
Actual mass of 1 atom of an element = atomic mass in amu × 1.66 × 10−24 g
Molecular mass
The molecular mass of a substance is a number which states that how many times mass of one molecule of a substance is heavier in comparison to 1/12th mass of one atom of carbon-12.
Constituents of an atom
The fundamental particles of an atom are electron, proton, and neutron.
Electron
- Electron had been discovered by J.J. Thomson.
- An electron was obtained from cathode rays experiments.
- The name of electron was given by Stoney.
- The relative charge on electron is −1 unit.
- The absolute charge value is − 1.6 × 10−19 Coulomb or − 4.8 × 10−10 e.s.u. (electrostatic unit).
- The relative mass of an electron is 0.000543 amu.
- The absolute mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 Kg.
- The charge/mass (e/m) ratio of an electron is − 1.76 × 10−8 Coulomb/gram.
Proton
- A proton had been discovered by Goldstein.
- A proton was obtained from anode rays experiments.
- The name of proton was given by Rutherford.
- The relative charge on proton is +1 unit.
- The absolute charge value is + 1.6 × 10−19 Coulomb or + 4.8 × 10−10 e.s.u. (electrostatic unit).
- The relative mass of a proton is 1.00763 amu.
- The absolute mass of a proton is 1.673 × 10−27 Kg.
- The charge/mass (e/m) ratio of a proton is 9.58 × 104 Coulomb/gram.
Neutron
- A neutron had been discovered by James Chadwick.
- A neutron was obtained from radioactivity phenomenon.
- The charge on neutron is 0 unit.
- The relative mass of a neutron is 1.00863 amu.
- The absolute mass of a neutron is 1.675 × 10−27 Kg.
- The charge/mass (e/m) ratio of a neutron is 0.
Atomic number
The number of proton or electron in an atom of the element is called atomic number. It is denoted by Z.
Mass number
The sum of number of protons and neutrons in an atom of the elements is called as mass number. It is denoted as A.
A = p + n
where A = mass number
p = number of protons
n = number of neutrons
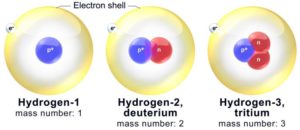
Isotopes: These are atoms of the elements having the same atomic number but different mass number.
In isotopes number of protons and electrons are same but number of neutrons are different. Example,
![]()
![]()
Isobars: These are atoms of the elements having the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
![]()
Isotones: These are atoms of different elements having the same number of neutrons.
![]()
Isoelectronic: These are atoms/molecules/ions containing the same number of electrons.