NFC stands for Near Field Communication. NFC is a short range, low-speed set of wireless communication protocols for exchange of data between two electronic devices. The range of NFC is about 4 cm or less. They can be used for contact less payments using mobile handsets without the use of any credit or debit card. NFC can be used for sharing a small-sized file or even bootstrapping more capable wireless connections so that larger files such as photos, videos and other such files can be shared.
How does NFC work?
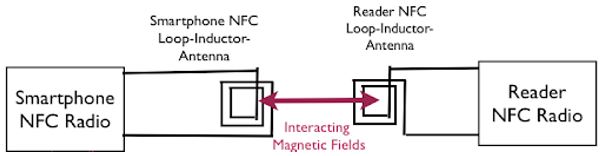
This short-range, low-speed wireless technology works on the concepts of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technique based on the principles of electromagnetic induction for transmitting messages. It uses radio waves for sending and receiving data. It uses two magnetic induction between two loop antennas which are placed at each other’s ‘near field’. The technique uses an initiator and target. The initiator generates the Radio Frequency field which can supply power to the passive target.
There are basically two types of NFC devices – passive and active.
Passive devices do not need any power source of their own. These types of passive devices have tags and some transmitters or antennas. They can send information to other NFC compatible devices through these antennas but they cannot connect to other passive NFC devices on their own.
Active devices can exchange data as well as establish a new connection with other active NFC devices. Examples of active NFC devices are public transport card readers and touch payment terminals. NFC uses transmission frequency of 13.56 MHz . NFC operates in three different modes.
- Peer to peer mode – It is widely used in smartphones and allows NFC-enabled smartphones and devices to exchange data between each other.
- Read/Write mode – It is a one-way transmission. In this mode NFC device can link with another NFC device to read or write from it.
- Card emulation mode – In this mode the NFC device can act as a means of contact less payment mode without the use of any credit/debit card.
NFC applications can be categorized as
- Touch and Go
- Touch and Confirm
- Touch and Connect
Touch and Go – It is used in application such as picking up Internet URL from a smart label on a poster. In this the user only needs to bring his device closer to the access code on the poster.
Touch and Confirm – In this the device user has to confirm the interaction by accepting the transaction or entering a password.
Touch and Connect – It enables peer to peer transfer between two NFC-enabled devices such as exchanging of documents, a music video or an image.
Advantages of NFC
- It is highly convenient to the user as the data exchange can be conveniently done just by bringing the two NFC-enabled devices closer.
- Cost of electronic issuance is greatly reduced.
- Communication is highly secured due to the close proximity of the devices.
- There is no special software required for this type of data exchange.
- No manual setting or configuration is required.
- No device search and pairing procedure is required.
Examples of devices using NFC technology
- Galaxy Nexus
- Galaxy Nexus S 4G
- Samsung Galaxy S II
- Samsung Galaxy Note
- Nexus S
- Nokia 6212 Classic
- Nokia 6131 NFC
NFC vs RFID
Though both RFID and NFC are based on the same underlying technology there ate some distinguishing features between them. NFC is a subset of RFID technology. Both uses radio waves for data transmission. NFC operates within the High Frequency range of the RFID spectrum. RFID is a much older technology and originated way back in the 1980s. NFC is a newbie and came int picture in 2002. RFID improves upon printed barcodes whereas NFC improves upon QR codes. Both technologies do not need line of sight operation but NFC has added Intelligence and is much efficient than the RFID. RFID can store and transmit simple IDs whereas NFC can transmit multiple data types.
NFC can provide solutions to solve all the challenges faced to implement Internet of Things applications – to connect the unconnected. It provides easy network access and data sharing between IoT devices. It provides secured data transmission within a closed proximity and hence hackers have less chance to hack them. Today, NFC is playing a key role in making the IoT applications more efficient.
Author
Anupama kumari
M.Tech (VLSI Design and Embedded system)
BS Abdur Rahman University
