A switch is an electrical component that can “make” or “break” an electrical circuit. A switch mainly works with ON and OFF mechanism.
Types of Switches
1. Ideal Switch
2. Practical Switch
Ideal Switch
1. It should have zero resistance or zero voltage drop in ON state and infinite resistance or zero current during OFF state. In other words, power loss across the switch should be zero both in ON and OFF state.
2. It should be closed and open instantaneously independent of current through it.
3. In the closed state, it should conduct current in one direction only. The resistance to reverse direction must be infinite.
During ON state
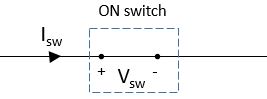
here Isw = switch current, Vsw = voltage across switch, and Psw = Switch power loss
Vsw = 0 Volt (always)
Isw = value depending upon the circuit condition
Psw = Vsw × Isw = 0 Watt
turn on time, ton = 0 seconds
During OFF state

Vsw = value depending upon the circuit condition
Isw = 0 Amp (always)
Psw = Vsw × Isw= 0 Watt
turn off time, toff = 0 seconds
Consider OFF switch condition as shown in figure 1.
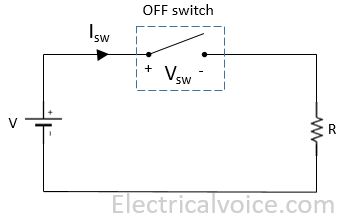
Vsw = V volt
Isw = 0 Amp
Psw = Vsw × Isw = 0 Watt
turn off time, toff = 0 seconds
Consider ON switch condition as shown in figure 2.
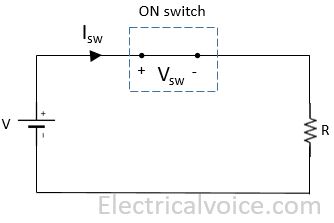
Vsw = 0 Volt
Isw = (V/R) Amp
Psw = Vsw × Isw = 0 Watt
turn on time, ton = 0 seconds
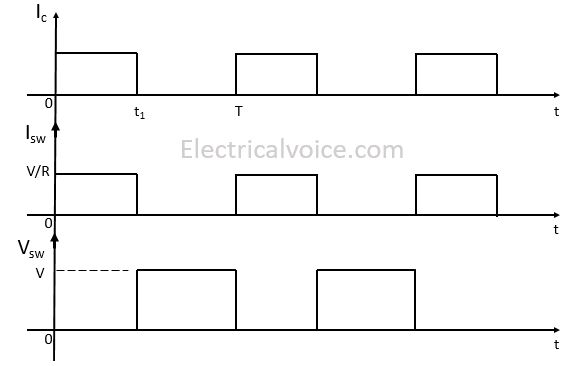
The switching characteristics of an ideal switch are shown below. Here Ic is the controlling signal that controls the ON and OFF of the switch. From time 0 to t1, the switch is closed (i.e. ON condition). From time t1 to T, the switch is open (i.e. OFF condition) and so on.
Practical Switch
1. A practical switch has non-zero resistance in ON state and finite resistance in the OFF state.
2. The time taken to the switch to change from OFF state to ON state i.e. turn ON time and turn OFF time is not same.
During ON state
Vsw ≠ 0 Volt
Isw = value depending upon the circuit condition
Psw = Vsw × Isw ≠ 0 Watt
turn on time, ton ≠ 0 seconds
During OFF state
Vsw = value depending upon the circuit condition
Isw ≠ 0 Amp
Psw = Vsw × Isw ≠ 0 Watt
turn off time, toff ≠ 0 seconds
The switching characteristics of a practical switch are shown below.
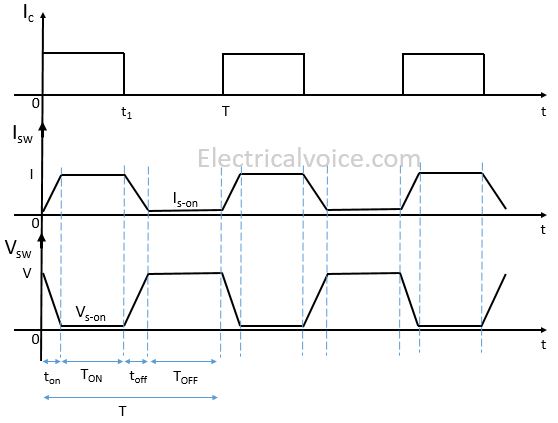
ton = The time taken to reach steady-state ON condition from the steady-state OFF condition.
TON = The time during which the switch remains in steady-state ON condition.
toff = The time taken to reach steady-state OFF condition from the steady-state ON condition.
TOFF = The time during which the switch remains in steady-state OFF condition.
T = Time period
T = ton + TON + toff + TOFF
Note: Normally the ON-state voltage drop across the switch and OFF-state leakage current through the switch are negligible as compared to circuit voltage and current. Hence may be neglected.
Losses in practical switch
1. ON-state loss
The power loss during the ON state of the switch is known as ON state loss. It is given by
Ps-ON = Vs-ON × Is-ON
2. OFF-state loss
The power loss during the OFF state of the switch is known as OFF state loss. It is given by
Ps-OFF = Vs-OFF × Is-OFF
3. Switching loss
Some power loss occurs in the switch when it changes state from ON to OFF state or OFF to ON state. These losses are combined together are called switching loss. It depends upon the turn ON and turn OFF time of the switch and also depends on the frequency of switching. As the turn On or turn OFF time increases, power loss increases. As the switching frequency increases, power loss increases.
