Millman’s Theorem
Case-1
The theorem states that if several ideal voltage sources V1, V2, V3,……., Vn in series with resistances R1, R2, R3,…….., Rn, are connected in parallel then the circuit may be replaced by a single voltage source Vout in series with the resistance Req. Let us consider a circuit having three sources i.e. n=3.
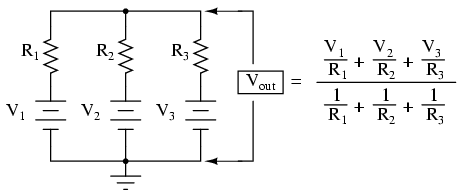
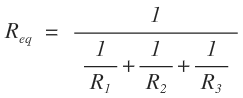
Case-2
The theorem states that if several ideal current sources I1, I2, I3,……., In are in parallel with resistances R1, R2, R3,…….., Rn, are connected in series then the circuit may be replaced by a single ideal current source I in parallel with the resistance Req such that
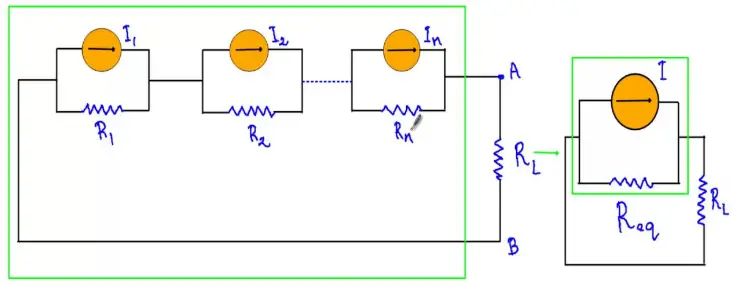
where
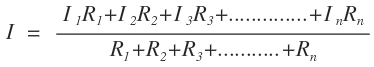
Req = R1+R2+R3+………………………+Rn
Limitations of Millman’s Theorem
1. Not applicable to the circuits consisting of impedances between the independent source.
2. Not applicable to the circuits consisting of dependent source between the independent source.
3. Not useful to the circuits consisting of less than two independent sources.
Applications & Advantages of Millman’s Theorem
1. This Theorem is very convenient for determining the voltage across a set of parallel branches, where there are enough voltage sources present to prevent solution via regular series-parallel reduction method.
2. It is easy to apply as it doesn’t require the use of simultaneous equations.
3. The Millman theorem is mostly applied for circuits with several operational amplifiers representing complex circuit topology.

where is about maximum power transfer theorem ???????????????????????
Thanks