Meissner’s Effect
Contents
show
The repulsion of magnetic flux from the interior of a piece of superconducting material as the material undergoes to the transition to the superconducting phase is known as Meissner’s Effect.
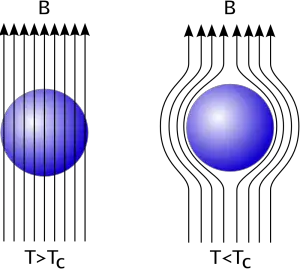
In superconductor
B = 0
µo( H + M ) = 0
M = − H ……………………. (1)
Also, M = χmH ……………. (2)
from (1) & (2)
χmH = − H
χm = − 1 ……………………. (3)
Since, χm = µr − 1 ………… (4)
from (3) & (4)
µr = 0 (Perfect diamagnetism)
Silsbee Rule
If a superconducting material causes a current such that magnetic field which it produced is equal to the critical field, the superconductivity disappears.
- The current density at which the superconductivity disappears is known as critical current density.
- This rule prevents the use of superconductor as coils for the production of the strong magnetic field.
- The magnetic field requires destroying the superconductivity need not be an external field; it may be internal magnetic field as well.
