A voltage telemetry system transmits the measured variable as a function of AC or DC voltage. A slide wire potentiometer is connected in series with the battery. The signal transmitting medium is essentially a copper wireline. A voltage telemetry system is shown in Fig. 1.
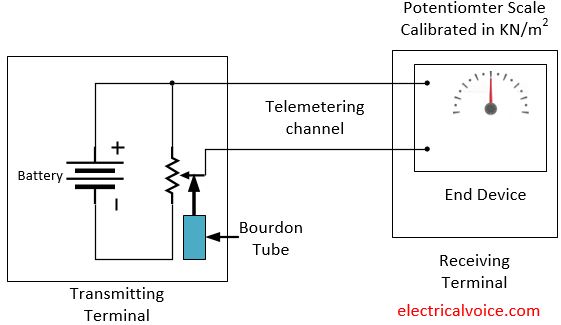
The sliding contact is positioned by a pressure sensitive, Bourdon tube. The telemetric channel consists of a pair of wires connected to a voltage measuring device such as a voltmeter or a null balance DC potentiometer indicator.
As pressure changes the Bourdon tube actuates the sliding contact thereby changing the voltage at the receiving end. The DC null balance potentiometer measures the voltage and positions the pointer on the scale calibrated in terms of pressure being measured. The use of null balance DC potentiometer reduces the current carried by the channel.
Voltage telemetry systems are related to the distance of about 300 m. Self-balancing potentiometers are usually used at the receiving end.
Advantages of Voltage Telemetry System
1. This type of telemetry system is satisfactory for adding several output voltages in series with the condition that the measurement is linear.
2. It is effective for short distance measurement.
3. Voltage can be easily transmitted.
4. The circuitry required is simple.
5. A wide variety of primary sensing elements are available to measure required variable.
Disadvantages of Voltage Telemetry System
1. It requires high-quality circuits.
2. Signal to noise ratio must be comparatively high. Since power level is small in voltage telemetry system. The transmission channel must be protected from sources of interference which are of the same order as that of the signal.
3. Relatively expensive
4. Not suitable for the use of many receivers working at the same time.
