The performance of a transformer can be determined with the help of two important performance indicators i.e. transformer efficiency and transformer voltage regulation. In this article, we will see what is transformer efficiency. We will also derive the condition of maximum efficiency.
Transformer Efficiency Definition
The efficiency of a transformer is defined as the ratio of output power to input power. The efficiency (η) formula is given as
$\eta =\frac{\text{Output Power}}{\text{Input Power}}$
The efficiency (η) formula in percentage is given as
% Efficiency,
$\eta =\frac{\text{Output Power}}{\text{Input Power}} \times 100$
As we know that,
Input power = Output power + Losses
∴ Input power = Output power + Copper loss + Iron loss
Now the % efficiency formula becomes
$\eta =\frac{\text{Output Power}}{\text{Output power + Copper loss + Iron loss}} \times 100$
It is noted that a transformer does not consist of any rotating parts. Hence there are no rotational or frictional losses. This is the reason why the efficiency of a transformer is very high. The efficiency of a well-designed transformer may be as high as 99%.
General Expression for Efficiency of transformer
When the transformer is fully loaded then
Output power in Watt at full load = V2I2cosφ
where, V2 is the secondary terminal voltage in volts
I2 is the secondary full load current in amperes, and
cosφ is the power factor of the load
The output power in kW at full load is
$\frac{V_{2}I_{2}}{1000}\cos \phi$
As we know that,
$S_{fl}=\frac{V_{2}I_{2}}{1000}$
Sfl is the full load kVA rating
∴ The output power in kW at full load = Sfl cosφ
Therefore, the efficiency of the transformer at full load is given as
$\eta _{fl}=\frac{S_{fl}\cos \phi }{S_{fl}\cos \phi\: +\: losses}\times 100$
Now if want to find the efficiency of the transformer at x% of full load, we can find it as follows.
The output power in kW at x% of full load = x × Sfl cosφ
Let Wc be the copper loss in kW at full load and Wi be the iron loss in kW.
As we know that copper losses are I2R.
copper losses are directly proportional to the square of load current and load current is proportional to loading (x%) i.e.
copper loss ∝ I2 ∝ x2
∴ Copper losses in kW at x% of full load = x2 Wc
and
Iron loss in kW at x% of full load = Wi (since the iron loss is constant)
Therefore, the efficiency of a transformer at x% of full load is given as
$\eta _{x}=\frac{x\; S_{fl}\cos \phi }{x\; S_{fl}\cos \phi\: +\: W_{i}+\: x^{2}W_{c}}\times 100$
This is the general expression for the efficiency of a transformer at x% of full load.
From the above formula, it may be concluded that the efficiency of a transformer depends upon % of loading, power factor of the load.
Condition for maximum efficiency of transformer
As we know that efficiency of a transformer in per unit at the load current, I2 is given by
$\eta =\frac{V_{2}I_{2}\cos \phi }{V_{2}I_{2}\cos \phi \: +\: W_{i}+\: W_{c}}$
Wc = I22R02
where, R02 is the total effective resistance of the transformer as referred to secondary.
Therefore,
$\eta =\frac{V_{2}I_{2}\cos \phi }{V_{2}I_{2}\cos \phi \: +\: W_{i}+\: I_{2}^{2}R_{02}}$
Dividing the numerator and denominator by I2,
$\eta =\frac{V_{2}\cos \phi }{V_{2}\cos \phi \: +\: \frac{W_{i}}{I_{2}}+\: I_{2}R_{02}}=\frac{N}{D}$
The efficiency will be maximum at a certain load current I2 for which the denominator is minimum.
So, we have to differentiate the denominator with respect to I2 and equate it to zero.
Therefore,
$\frac{\mathrm{d} }{\mathrm{d} I_{2}}\left ( V_{2}\cos \phi +\frac{W_{i}}{I_{2}}+I_{2}R_{02} \right )=0\\ \Rightarrow \left ( 0-\frac{W_{i}}{I_{2}^{2}}+R_{02} \right )=0\\ \Rightarrow W_{i}=I_{2}^{2}R_{02}$
i.e.
Iron loss (Wi) is equal to copper loss (I22R02).
In other words, we can say that fixed (or constant) losses = variable losses.
∴ the condition for maximum efficiency of a transformer is Iron loss equals Copper loss.
Now will find the percentage of loading x at which maximum efficiency occurs.
Let Wc be the copper loss in kW at full load and Wi be the iron loss in kW.
As we know from previous results, the efficiency of a transformer is maximum when copper loss equals iron loss.
Let efficiency is maximum at x% load.
The Copper loss in kW at x% load = x2Wc
The Iron loss in kW at x% load = Wi
∴ When the efficiency is maximum, x2Wc = Wi
OR
$\Rightarrow x^{2} = \frac{W_i}{W_c}$
∴ % of load at which maximum efficiency occurs is
$x=\sqrt{\frac{W_i}{W_c}}$
where, Wi is the iron loss at no load and Wc is the copper loss at full load.
Transformer efficiency vs load curve
The following diagram shows the variation of efficiency with % change in load. The maximum efficiency of the transformer occurs when copper loss equals iron loss. This curve also shows the variation of iron losses and copper losses with % change in load.
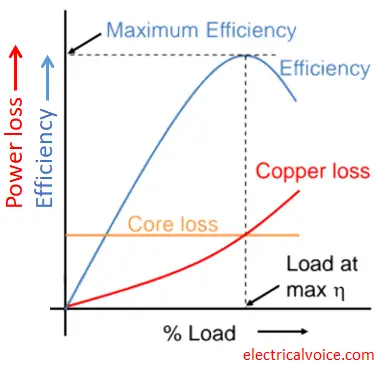
Generally, transformers are designed such that their maximum efficiency occurs near the rated load. It means the efficiency is maximum if the transformer is operating near its rated load.

Reasoning and Maths is all very clear in this Article.
I have learnt (elsewhere) that Maximum Output from a Transformer occurs when V (out on load) is 1/2 V out at no load conditions.