Thermal Power Station
A thermal power station is a power plant in which the prime mover is steam driven.
The operation of a thermal power station is such that the water is heated first, and turns into steam. This steam is used for rotating a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After passing through the turbine, the steam is condensed in a condenser; this is called as a Rankine cycle. The variation in the design of thermal power stations depends on the different fuel sources. Some countries prefer to use the term energy center in place of the power plant because such facilities convert forms of heat energy into electrical energy. The term power plant is the most common in the United States (US), while power station term is common in many Commonwealth countries and especially in the United Kingdom (UK).
Almost all coal, geothermal, nuclear, solar thermal electric, and waste incineration plants, as well as many natural gas power plants, are thermal.
Coal-fired thermal power station
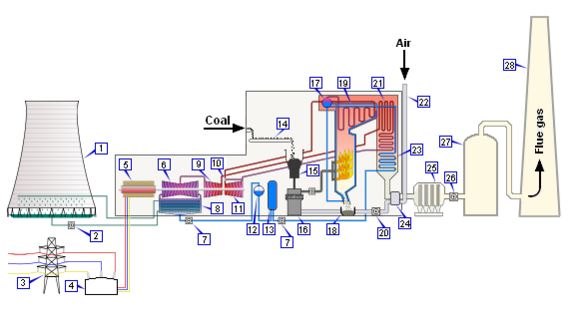
| 1. Cooling tower | 10. Steam control valve | 19. Superheater |
| 2. Cooling water pump | 11. High-pressure steam turbine | 20. Forced draught (draft) fan |
| 3. Three-phase transmission line | 12. De-aerator | 21. Re-heater |
| 4. Step-up transformer | 13. Feed water heater | 22. Combustion air intake |
| 5. Electrical generator | 14. Coal conveyor | 23. Economizer |
| 6. Low-pressure steam turbine | 15. Coal hopper | 24. Air pre-heater |
| 7. Boiler feed water pump | 16. Coal pulverize | 25. Precipitator |
| 8. Surface condenser | 17. Boiler steam drum | 26. Induced draught (draft) fan |
| 9. Intermediate pressure steam turbine | 18. Bottom ash hopper | 27. Flue gas stack |

You have 28 parts and have labeled 27. Is #27 the flue gas stack, or is that the answer for #28?