A transformer is an important device used for stepping up or stepping down voltage or current without changing the frequency. It is a highly efficient device due to the absence of rotating parts. There are different parts of transformer. In this article, we will see the transformer parts and their functions.
Let see each part and their functions in details.
Different Parts of Transformer and their functions
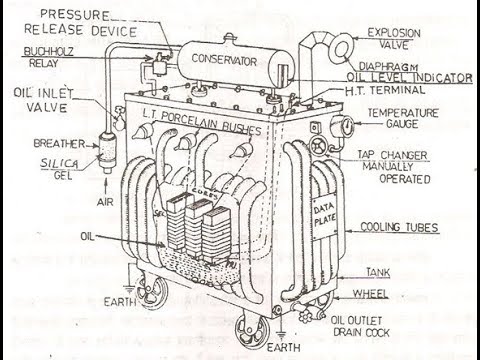
The following is the list of transformer parts.
- Laminated core
- Windings
- Insulating materials
- Transformer oil
- Conservator tank
- Buchholz Relay
- Breather
- Cooling tubes
- Tap Changer
- Explosion vent
1. Laminated core
The main function of a laminated core is to separate primary and secondary windings. The core is laminated in order to reduce the core losses in a transformer. The core is generally made up of Cold Rolled Grain Oriented (CRGO) steel material.
The other function of the laminated core is to allow the set up of magnetic flux in the transformer by providing a low reluctance path and thus helps in flux linkage with the windings.
2. Windings
Generally, copper windings are used in the transformers. The main function of windings is to produce magnetic flux and induce mutual EMFs. These windings carry high voltage and current through them.
3. Insulating materials
The main function of insulating material is to provide insulation to windings so that it does not come in contact with the transformer core or other conducting material. The windings are wrapped in insulating paper or cloth.
4. Transformer oil
The main function of the transformer oil is to provide insulation as well as act as a cooling agent due to its chemical properties and dielectric strength. It dissipates heat generated from the core and windings to the environment. Hence cooling the transformer.
5. Conservator tank
The main function of a conservator tank is to provide extra space to accommodate the transformer oil during oil expansion inside the transformer when the ambient temperature rises. It is a cylindrical tank mounted on the top of the supporting structure of a transformer. It is generally half-filled with transformer oil.
6. Buchholz relay
The main function of the Buchholz relay is to protect the transformer from different internal faults such as inter-turn fault, short circuit fault, etc. It detects the occurrence of a fault and generates the alarm circuit. It is present between the main tank and the conservator tank.
You can read about the basic working of a Buchholz Relay in this article.
7. Breather
The main function of a breather is to prevent moisture to enter the transformer during the breathing cycle of a transformer. It contains the silica gel that absorbs the moisture from the air and hence prevents transformer oil to contaminate and thereby saves the internal parts.
8. Cooling tubes
The main function of the cooling tubes is to transfer heat from the transformer core and coils to the environment. The heated transformer oil circulates through the cooling tubes where the heat radiates out by natural airflow and hence cooling the transformer oil.
9. Tap Changer
The main function of the tap changer is to regulate the transformer output voltage by altering the number of turns in one winding and thereby changing the turn ratio of the transformer.
10. Explosion vent
The main function of the explosion vent is to provide protection against excessive pressure build-up in the transformer during heavy internal faults. It allows releasing hot boiling transformer oil in order to avoid the explosion of the transformer.

well explained ,,