Hydro energy or hydraulic energy is the energy of moving water which is obtained when the gravitational descent of a river is compressed from a long run to a single location with a dam or a flume. It is not only a clean and non-polluting source of energy, but also one of the most important sources of energy next only to thermal energy.
In the hydro power plant, a turbine converts the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy, which is coupled with a generator that converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy. In the hydro power plant, a turbine converts the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy, which is coupled with a generator that converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy.
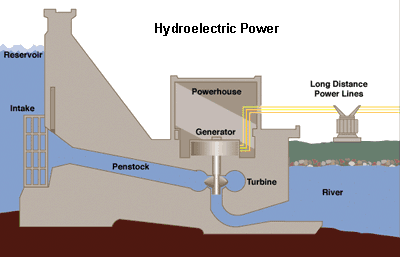
Hydropower projects are generally categorized in two segments:
(i) Small hydro project (SHP)
(ii) Large hydro project (LHP)
In India, hydro projects upto 25 MW station capacity have been categorized as small hydro power (SHP) or micro-hydro power projects. These projects have been increasingly used as an alternative energy source, especially in remote areas where other power sources are not feasible. A small hydro project can be installed in small rivers or streams with little or no environmental effect on activities such as fish migration.
Large scale hydropower plants are generally developed to produce electricity for government or electric utility projects. These plants are more than 30 MW in size and use a dam or reservoir to retain water from river.
Advantages of Hydro Energy
- Hydro energy is a renewable resource in which electricity can be generated constantly as long as sufficient water is available.
- Hydroelectric power plant produces no primary waste or pollution.
- It has low operating and maintenance cost.
- It has a short gestation period.
Limitations of Hydro Energy
- Hydro power plants can only be installed in those areas where there is sufficient supply of water.
- The hydro power plants can induce flooding or submerges large forests (if they have not been harvested). The resulting anaerobic decomposition of the carboniferous materials releases methane, which is a greenhouse gas.
- These plants rarely erected near load centers, requiring long transmission lines.
- During low-demand periods, it keeps producing electricity which leads to loss of power.
image source: mpoweruk.com/hydro_power.htm
