In this article, we will learn important terms in Economic Aspects of Power Generation.
What is Load?
A device which uses electrical energy is said to impose a load on the system.
What is Connected Load?
The sum of continuous ratings of all loads connected to the system is known as a connected load.
What is Demand?
It is the load that is drawn from the source of supply at the receiving terminals averaged over a suitable and specified interval of time.
What is Installed Capacity?
The arithmetic sum of ratings of alternators connected to a bus is called as installed capacity.
What is Demand Interval?
It is the period over which the load is averaged.
There are two types of demands:
1. Instantaneous demand
2. Sustained demand
What is Maximum demand?
It is also called as peak demand. It is the greatest of all demands which have occurred during the specified interval of time.
- It helps in determining the installed capacity of a generating station.
- The Cost of plant and equipment increases with the increase in maximum demand.
What is Average load?
Average load = (Energy consumed ÷ total number of hours)
Note: average load < maximum demand < installed capacity
What is Reserve capacity?
Reserve Capacity = Installed capacity − maximum demand
What is Demand Factor?
It is the ratio of actual maximum demand of the system to the total connected load of the system.
- The demand factor depends upon the nature of the load.
- Lighting loads have higher demand factors than power loads.
- The demand factor is usually less than 1.
What is Average Demand?
It is also called as an Average load. It is the ratio of energy consumed in a given period of time to the number of hours in that time period.
What is plant Load Factor?
It is the ratio of the average load over a given period of time to the peak load (maximum demand) occurring during that period.
It can also be defined as the ratio of the actual energy consumed during a given period to the energy which would have been used if the maximum demand had been continuously maintained throughout that period.
- The higher the Load factor, the lesser will be the cost of generation per unit (kWh) for the same maximum demand.
What is Diversity Factor?
It is the ratio of the sum of the individual maximum demands of the various subdivisions of a system to the maximum demand of the whole system.
- Diversity factor can be defined for loads, substations, feeders, and generating stations.
- The diversity factor can be equal to or greater than 1.
- DF greater than 1 represents good diversity.
- DF equal to 1 represents poor diversity.
- Large diversity factor has the effect of reducing the maximum demand. Hence lesser plant capacity is required. As a result, capital investment on the plant is reduced and the cost of generation is also reduced.
- A high diversity factor may be obtained by using electrical energy at night or light load periods.
What is Load diversity?
It is the difference between the sum of the peaks of two or more individual loads and the peak of the combined load.
What is Utilization Factor?
It is the ratio of maximum demand of a system to the rated capacity of the system.
What is Plant Capacity Factor?
It is also known as the plant factor. It is the ratio of the total actual energy produced or supplied over a specified period of time to the energy that would have been produced or supplied if the plant (or unit) had operated continuously at maximum rating.
The maximum plant rating in the total installed plant capacity including the reverse capacity.
What is Loss Factor?
It is the ratio of the average power loss to the peak load power loss during the specified period of time.
Note: This relationship is applicable to the copper losses of the system but not for the iron losses.
What is Base load?
The base load on a grid is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time.
What is Peak load?
A sudden increase in the load above base load for a very short duration is called a peak load.
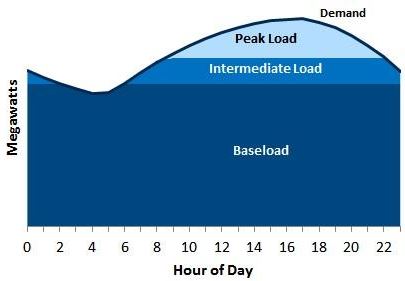
What is Firm Power?
The power available in the emergency condition is called as firm power.
What is Spinning Power?
The power available at the busbar and delivered to the load is called spinning power.
What is Cold Reserve?
The power available for service but not in operation is called a cold reserve.
What is Hot Reserve?
The power available for operation but not in service is called as a hot reserve.
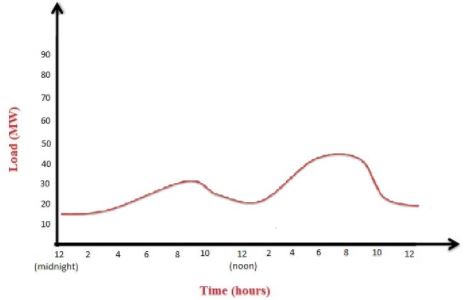
What is Load Curve?
The variation of the load with respect to time for specified duration graphically.
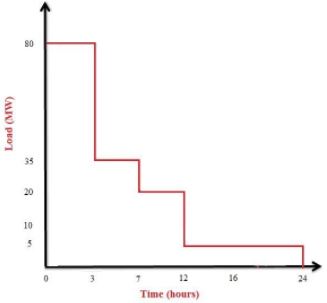
What is Load Duration Curve?
The variation of the load with respect to the time (or percentage of the time) and loads are arranged in descending order.
Questions & Answers
Q1. A 200 MW generator having a plant capacity factor and plant load factor is 60% and 80% respectively. The reserve capacity in MW as __________________?
Ans. Plant capacity factor (PCF) = 60% = 0.6
Plant load factor (PLF) = 80% = 0.8
PLF = (average load ÷ maximum load)
PCF = (average load ÷ installed capacity)
PLF ÷ PCF = (installed capacity ÷ maximum load)
0.8 ÷ 0.6 = (200 ÷ maximum load)
Therefore, maximum load = 150 MW
Reserve capacity = Installed capacity − maximum load = 200 − 150
Reserve capacity = 50 MW
