The data is transmitted from one place to other through different mediums. All transmission system has two devices i.e. transmitting and receiving end devices. These two devices are connected through a medium. there are two types of transmission i.e.
- Baseband transmission
- Broadband transmission
Baseband transmission
When data are sent without modulation, usually over wires or cables, it is called baseband transmission.
Broadband transmission
When data are modulated and sent through a wireless medium, it is called broadband transmission.
1. Wire Connections
- these are wires or trace on a printed circuit board (PCB).
- used in internal circuits or nearby devices like computer and/or peripherals.
- Used for very short distances.
2. Coaxial Cable
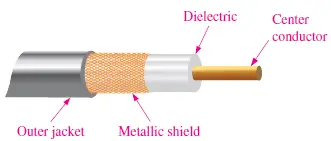
- Coaxial cable (coax) consists of a conductor, Dielectric, Metallic shield, and Outer jacket.
- The metallic shield protects the conductor against electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Used for frequency upto 1 GHz.
- Applications are cable TV and Internet connections.
3. Twisted Pair Cable
It is of two types,
- Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable
- Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable
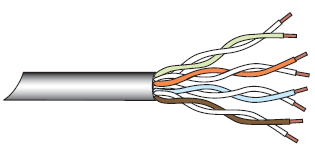
- The two wires in each pair are twisted so that they cross each other at nearly 90°. This will cancel the electromagnetic fields generated by the signals. Due to which Cross talk, a type of distortion, is minimized.
- UTP is color coded according to a standard 25-pair color code.
- Applications in indoor telephone lines, USB cables, computer networks, security cameras, etc.
- Used for frequency upto 1 MHz.
- STP cable is enclosed in a metal sleeve which provides more EMI protection as compared to UTP cable.
4. Optical Fiber Cable
The single optical fiber is shown in the figure below.
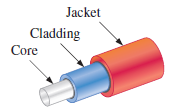
The Optical Fiber Cable consists of hundreds of single optical fiber. It is shown in the figure below.

- It uses light pulses transmitted through optical fibers.
- It works on the principle called total internal reflection.
- It has faster data rates, higher signal capacity (more signals at a time), and better transmission over longer distances.
- It is not susceptible to EMI.
- They are costly.
- It is used for telecommunication and networking for longer distance transmission.
- Used for frequency upto 100 GHz.
5. Wireless Transmission
- In this method, data is transferred through air and space via electromagnetic waves without the use of physical connections.
- Here the air is the transmission medium.
- Communications occur within the radio wave, microwave, and infrared frequencies.
