In modern measurement systems, the various components comprising the system are usually located at the distance from each other. It is, therefore, becomes necessary to transmit the data and information between them through some form of communication channel.
Telemetry may be defined as measurement at a distance.
Telemetry is indicating, recording, integrating a quantity at a distance by electrical means.
Telemetry is a technology which enables a user to collect data from several measurement points that are an inaccessible or inconvenient source, to transmit the data to a convenient location and present the several individual measurements in a usable form.
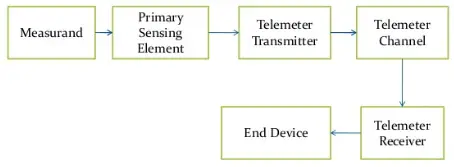
The general block diagram of a telemetry system is shown in fig.1. The telemetry system consists of the primary sensing element, telemeter transmitter, telemeter channel, telemeter receiver, and end device.
Q. Why it is necessary to use telemetry in an instrumentation system?
In modern measurement systems, the various components comprising the system are usually located at a distance from each other. It, therefore, becomes necessary to transmit the data or an information between them through some form of communication channels.
The transmission of a measured variable to a remote point is an important function in instrumentation system because of the size and complexity of modern industrial plants. The most common variables encountered in industrial plants are temperature, pressure and flow and transmission of data of these systems take great length from the place of measurement to the place of data recording or display. This will result in excessive measurement lags. Hence there is a need for fast transmission of data.
Classification of Telemetry (or data transmission)
1. On the basis of Domain
- Hydraulic transmission Telemetry
- Pneumatic Telemetry
- Electrical & Electronic Telemetry
2. On the basis of characteristics of an electrical signal
- Current Telemetry
- Voltage Telemetry
- Frequency Telemetry
- Position Telemetry
- Pulse Telemetry
3. On the basis of the type of transmission
- Analog Telemetry
- Digital Telemetry
4. On the basis of Distance
- Short distance Telemetry
- Long distance Telemetry
