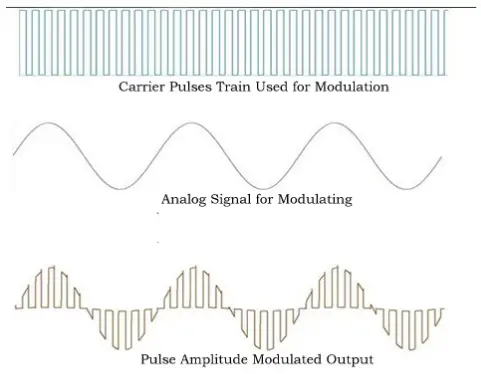
Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) is a type of pulse modulation in which the signal is sampled at regular intervals, with each sample proportional to the amplitude of the signal at the time of sampling.
There are two types of Pulse Amplitude Modulation
- Single polarity PAM
- Double polarity PAM
Single polarity PAM
In this type of PAM, a fixed DC level is added to the signal so that pulses are always positive.
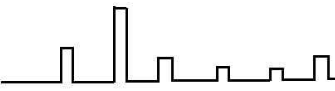
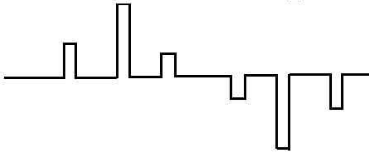
Double polarity PAM
In this type of PAM, the signal after PAM has positive and negative polarity.
How to generate PAM
Initially, the signal is fed to one input of the AND gate. On the other input, pulses at the sampling frequency are applied. the output of AND gate is pulses at the sampling rate. The amplitude is equal to the signal voltage at the sampling instant. finally, Gate output is given to the pulse shaping circuit. The pulse shaping circuit makes the voltage profile a flat top.
Advantages of Pulse Amplitude Modulation
- Easy to generate
- Easy to demodulate
Disadvantages of Pulse Amplitude Modulation
- Since PAM does not have constant amplitude, this type of pulse modulated signal is not noise immune. Hence it is less frequently used.
