Power electronics is a combination of two main branches of engineering i.e. power and electronics engineering. Power engineering deals with the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electric energy at high power level whereas electronic engineering deals with the production, transmission, and reception of signals & data at the low power level.
Power engineering machines/apparatus are mainly based on electromagnetic principle whereas electronics engineering devices are based upon the phenomenon occurring in semiconductors, vacuum, etc.
Power electronics referred to that field of study which applies the application of electronic principles into situations that are rated at high power level rather than the signal level (low power level).
Example: semiconductor power switches like SCR, thyristors, MCT, GTO’s, etc. work on the principle of electronics (movement of electrons and holes) but have high power ratings.
The block diagram below shows the components of a power electronics system and how they are interlinked.
Block diagram
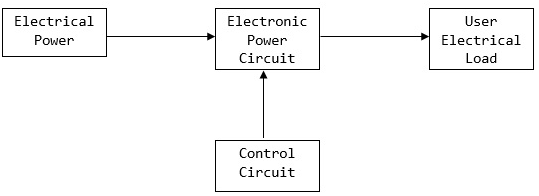
Power Electronics system converts electrical energy from one form to another and ensure the following is achieved
- Maximum efficiency
- Maximum reliability
- Maximum availability
- Minimum cost
- Least weight
- Small size
Applications of Power Electronics
Power electronics find applications in aerospace, commercial devices, industries, telecommunications, transportations, utility systems, etc.
1. Aerospace
space shuttle power supply systems, satellite power systems, Aircraft power systems.
2. Commercial
Heating, Ventilating, and air conditioning, central refrigeration, lighting, computers and office equipment, Uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs), elevators.
3. Industrial
pumps, compressors, blowers and fans, machine tools (robots), arc furnaces, induction furnaces, lighting, industrial lasers, induction heating, welding.
4. Telecommunications
Battery chargers, power supplies (DC and UPS).
5. Transportation
Traction control of electric vehicles, battery chargers for electric vehicles, electric locomotives, streetcars, trolley buses, subways, automotive electronics including engine controls.
6. Utility Systems
High voltage dc transmission (HVDC), static var compensation (SVC), supplemental energy sources (wind, photovoltaic), fuel cells, energy storage systems, induced draft fans and boiler feedwater pumps.
7. Residential
refrigeration and freezers, space heating, air conditioning, cooking, lighting, electronics (personal computers, other entertainment equipment).

Topic bhut acche by single phase halfwave with freewheel diode ki BHI notes send kri