Q. Write an 8085 program and draw a flowchart to Sort the array in Descending Order.(8085 Microprocessor Program)
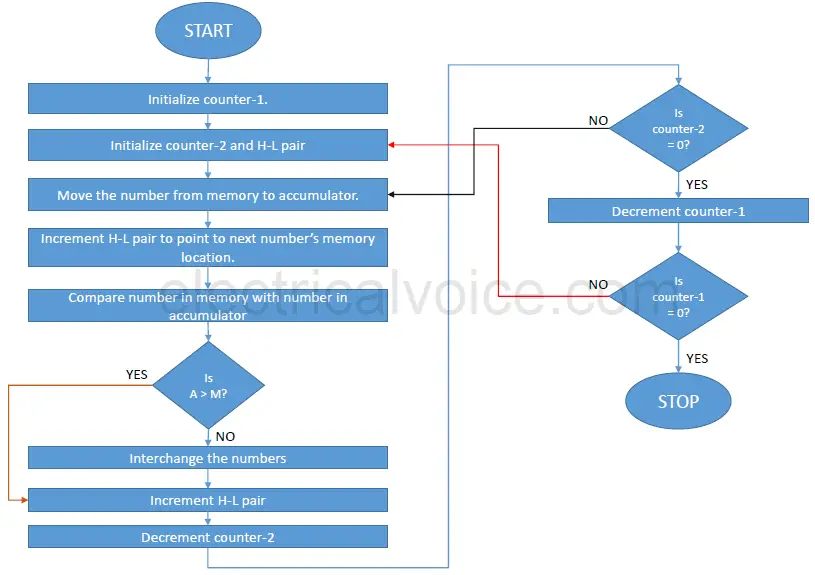
Flowchart/Algorithm
Program
| Address | Mnemonics | Operand | Opcode | Comments |
| 2000 | MVI | B, 05H | 06 | Initialize counter-1. |
| 2001 | 05 | |||
| 2002 | MVI | C, 05H | 0E | Initialize counter-2. |
| 2003 | 05 | |||
| 2004 | LXI | H, 3000H | 21 | Load H-L pair with address 3000H. |
| 2005 | 00 | |||
| 2006 | 30 | |||
| 2007 | MOV | A, M | 7E | Move the number from memory to reg. A. |
| 2008 | INX | H | 23 | Increment H-L pair. |
| 2009 | CMP | M | BD | Compare the number with next number. |
| 200A | JNC | 2015H | D2 | Don’t interchange if number > next number. |
| 200B | 15 | |||
| 200C | 20 | |||
| 200D | JZ | 2015H | CA | Don’t interchange if number = next number. |
| 200E | 15 | |||
| 200F | 20 | |||
| 2010 | MOV | D, M | 56 | Otherwise, swap the numbers. Move next number from memory to D. |
| 2011 | MOV | M, A | 77 | Move the first number from A to memory. |
| 2012 | DCX | H | 2B | Decrement H-L pair. |
| 2013 | MOV | M, D | 72 | Move next number from D to memory. |
| 2014 | INX | H | 23 | Increment H-L pair. |
| 2015 | DCR | C | 0D | Decrement counter 2. |
| 2016 | JNZ | 2007H | C2 | If counter-2 ≠ 0, repeat. |
| 2017 | 07 | |||
| 2018 | 20 | |||
| 2019 | DCR | B | 05 | Decrement counter-1. |
| 201A | JNZ | 2002 | C2 | If counter-1 ≠ 0, repeat. |
| 201B | 02 | |||
| 201C | 20 | |||
| 201D | HLT | 76 | Halt |
Output
Before Execution:
3000H: 05H
3001H: 15H
3002H: 01H
3003H: 65H
3004H: 32H
After Execution:
3000H: 65H
3001H: 32H
3002H: 15H
3003H: 05H
3004H: 01H
Program Explanation
- This program sorts an array in descending order.
- Let us assume that there are five numbers in the array and its starting address is 3000H.
- Initially, counter-1 and counter-2 are initialized with the size of the array.
- H-L pair is pointed to the starting address of the array.
- In the first iteration, the first number is compared with the second number.
- If first number > second number, then do not interchange them. Otherwise, if the first number < second number, then swap them.
- In the next iteration, the first number is compared with the third number.
- If first number > third number, then do not interchange them. Otherwise, if the first number < third number, then swap them.
- In the next iteration, the first number is compared with the fourth number and the process continues until counter-2 becomes zero.
- When counter-2 becomes zero, counter-1 is decremented and the process continues until all the numbers are arranged in descending order.
