Magnetic flux is defined as the number of magnetic lines of force passing normally through a surface. It is denoted by symbol Φ (phi). The S.I. unit of magnetic flux is weber (Wb). It is a scalar quantity. The CGS unit of magnetic flux is maxwell. Consider a surface having area, A in the magnetic field having magnetic flux density, ![]() as shown in figure 1.
as shown in figure 1.
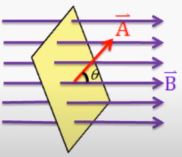
Mathematically, Magnetic flux is defined as the scalar product between the magnetic flux density (![]() ) and the vector of the surface area (
) and the vector of the surface area (![]() ).
).
![]()
where,
![]() = magnetic flux
= magnetic flux
B = magnetic flux density magnitude
A = area of surface
θ = angle between ![]() and
and ![]()
Note: The direction of the vector ![]() is always normal to the surface.
is always normal to the surface.
Case-1: When θ = 0°
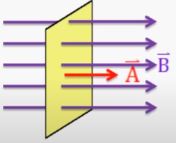
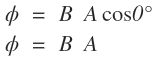
In this case, the flux is maximum.
Case-2: When θ = 90°
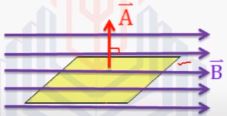
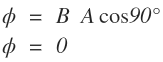
In this case, the flux is minimum.
Note: Magnetic flux is usually measured with a fluxmeter.
