 |
| Fig. Overhead Line Insulators |
Overhead Line Insulators are used to separate line conductors from each other and from the supporting structures or towers electrically.
Desired properties of Overhead Line Insulators
1. Insulator should have high mechanical strength to hold the conductor load under worst condition.
2. Insulator should have high permittivity (high dielectric strength) for withstanding high electrical stress.
3. The insulator should not be porous and free from cracks.
4. It should have high resistance to temperature.
5. Minimum leakage current to earth to keep radio interference and corona loss within an acceptable limit.
There are some important terms related to insulators that we discussed before going to the topic on Types of Insulator.
Electrical failure of Overhead Insulators
1. Puncture
It is the phenomenon in which an arc passes through the body of the insulator due to lightning or line surge. The insulator will get damaged by a puncture. So a new insulator unit is used in place of damaged one.
2. Flashover
It is the phenomenon in which an arc discharge between the conductor and earth through air surrounding the insulator due to lightning or line surge. The insulator is not damaged by a flashover. This can be reduced by using petticoats or rain sheds. This will increase the resistance to leakage currents.
Note: Flashover should occur before puncture.
3. Factor of Safety
The ratio of puncture voltage to flashover voltage is known as Factor of Safety. It should be high as possible.
Types of Insulators
1. Pin type insulator
2. Suspension type insulator
3. Strain or tension type insulator
Lets discussed these insulators one by one.
1. Pin type insulator
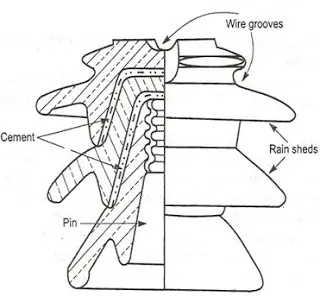 |
| Fig. Pin type insulator |
- Single piece type pin insulator used for lower voltage.
- 2 or 3 piece type pin insulator used for higher voltages. Two or three Single piece type pin insulator are joined together by cement to form 2 or 3 piece type pin insulator respectively.
- This type of insulator is used up to 33kV level due to increase in size, weight, and cost.
Advantages of Pin Insulator
1. As the voltage level increases, the size of insulator units increases. Hence they are economical up to a level below 33kV.
This type of insulators consists of a number of separate insulator units. These single units are connected to each other by metal links. This insulator is shown in the figure below.
 |
| Fig. Suspension Insulator |
The line conductor is attached to the last insulator unit. The string is suspended from the cross arm of the support structure. The operating voltage of each insulator unit is 11kV.
The usual number of discs insulators used in Suspension Insulators are
Voltage (kV): 66 132 220 400
Number of discs: 4-5 9-10 15-16 22-23
These type of insulators are used where there is a sharp turn or change in direction at an angle. At these positions, insulators encounter high mechanical stress. These are shown below.
 |
| Fig. Strain or Tension Insulator |
2. For higher voltage, suspension insulators are used in the horizontal direction.
Insulator Materials
1. Porcelain
2. Toughened Glass
3. Polymer
Usually, porcelain and toughened glass material are used as an insulator. Porcelain Insulators are brown in colour. Glass insulator has one disadvantage i.e. moisture condenses on its surface. There are also some advantages of toughened glass over porcelain such as
- Higher mechanical strength. Hence, there is less damage during transport and installation.
- Higher puncture strength compared to porcelain insulator.
- Long life
- High thermal shock resistance.
Polymer Insulator
Polymer Insulator is made up of fibre glass and an epoxy polymer in certain fixed quantities. It has been developed by General Electric company under the trade name “Gepol“. They have following advantages
- 70% lighter in weight compared to similar porcelain unit.
- High mechanical strength.
- High thermal shock resistance to reduce damage to flashover.
- Excellent radio interference voltage performance.

Very good article, detailed explanation