The electronics industry has faced various breakthroughs with the development of advanced materials and designs to cater to the demand for tinier and lighter devices. We now live in a world that heavily depends on electronics. Printed Circuit Boards or PCBs are the electronic boards that enable major functions of electronic devices. These functions include but are not limited to, switching, storing, sensing, and controlling. The pressure is constantly on to design and produce electronics that are smaller, thinner, and more lightweight.
A significant innovation in PCB technology is the emergence of rigid flex PCBs. In this article, we will learn more about rigid flex circuit boards, their advantages, and their impact on the modern world.
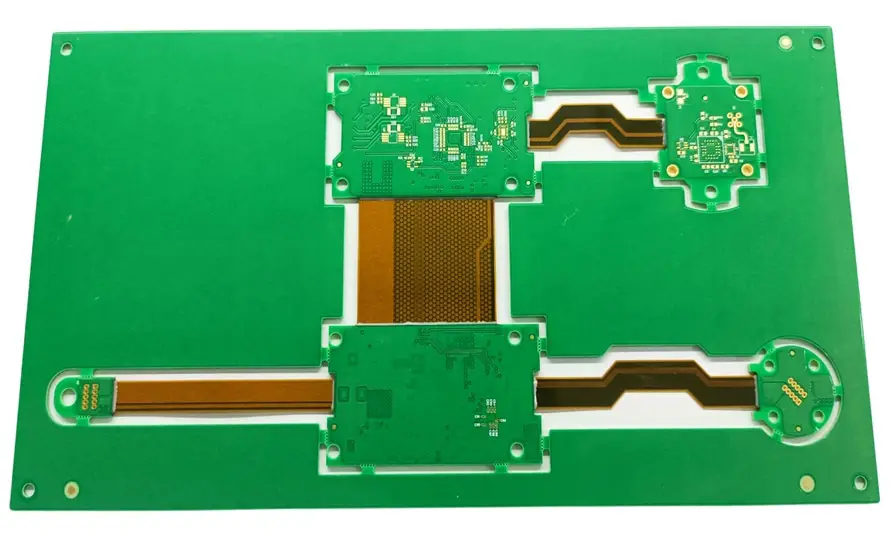
What are Rigid Flex PCBs?
A rigid flex PCB combines the strengths of flexible and rigid boards by integrating them into a single board design. This hybrid configuration allows for more stable structures with flexible sections to enable compact and lightweight designs. The rigid parts are where components are mounted while the flexible parts are the areas that are bent and folded to fit into spaces. Rigid-flex boards are also capable of mounting on both sides of the board.
The flexible layers of a rigid flex circuit board can be made from polymeric materials like polyimide and polyester, while the rigid sections can be composed of fibreglass epoxy such as FR4. Adhesive layers are used to laminate the rigid and flexible parts of the PCB. Critical considerations in the design of rigid-flex boards include bend radius, choice of material, and layer count to ensure excellent performance while in operation.
What are the Different Applications of Rigid-Flex PCB?
Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Boards provide a wise and practical approach to achieving a space-efficient and lightweight design.
Aerospace
Aerospace applications utilize advanced technology in building systems designed for harsh environments. Robotics in aerospace applications consists of myriads of boards including rigid-flex boards to optimize mass and volume that can withstand dynamic conditions.
Medical
Rigid-flex boards are also extensively used in medical applications where dynamic bending is required. Rigorous design rules related to medical applications should be complied with to ensure safe and reliable rigid-flex systems.
Consumer Electronics
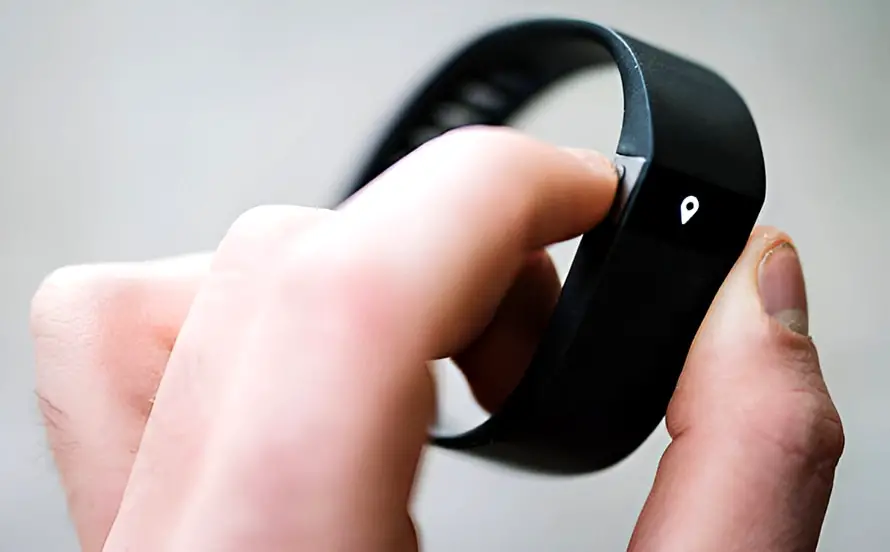
In consumer electronics, miniaturization is the primary trend. This can be met when using flexible and rigid-flex boards. Wearable devices such as smartphones and glasses require flexible and rigid-flex circuits that can fit into areas with space constraints. Computers also have internal components mounted on rigid-flex boards to have high-density designs.
Automotive
Automotive systems are also equipped with rigid-flex circuits that perform reliably. Parts of a modern vehicle with rigid-flex boards include infotainment systems, lighting, transmission controls, sensors, and safety systems.
Industrial
Industrial applications are also dependent on rigid-flex printed circuit boards such as machinery, control systems, and actuators. Power supply systems in industrial settings also have rigid-flex circuit boards that can carry high voltages.
Why Use Rigid-Flex PCBs?

Below are the known benefits of rigid flex PCB that make them a practical solution for many applications.
Space Maximization
Rigid boards pose certain design limitations, unlike rigid-flex boards that can conform to various geometric shapes and three-dimensional spaces. Instead of using connectors and space-consuming cables, rigid-flex circuit boards can be used to reduce the final footprint of an electronic device. As rigid-flex boards are thinner with fewer interconnects, the overall thickness is minimized which is suitable for wearables and mobile devices.
Reliability
Reliability is also one of its advantages due to the lesser requirement for connectors. Additional external connectors and cables can contribute to potential failures. The flexible sections can absorb vibrational stresses while the rigid sections provide structural rigidity enhancing their resistance to mechanical stresses. Rigid-flex circuit board has good signal integrity making it a good choice for high-frequency applications.
Design Flexibility
As rigid-flex circuit boards can be folded, bent, twisted, and even inserted into tight spaces, more room is open for design enhancements. They are much more favourable for compact and high-density designs. Not only that, rigid-flex boards can also have multiple layers based on the desired applications. Cost and performance are weighed against one another through the careful selection of a wide choice of flexible and rigid materials.
Cost Efficiency
The elimination of connectors and harnesses because of the utilization of rigid-flex boards also reduces materials and assembly costs. As also mentioned, failure points are reduced which also lessens the need to constantly replace defective parts. It is also more appealing to market and sell devices with more innovative designs which are made possible with rigid-flex circuit boards.
Versatility
Given the design flexibility of rigid-flex board, it is widely used in many applications from consumer to automotive and industrial markets. Electronic devices, such as laptops and mobile phones require electronic boards that are compact and lightweight and can be supported by rigid-flex circuit boards.
What are the Future Trends in Rigid-Flex PCB?

A lot of innovations are in store for rigid-flex circuit boards. PCB manufacturers should catch the soaring trend of PCB fabrication techniques and apply newborn techniques to the product. Below are some of the trends that are expected to rise in the field of rigid flex PCB.
Widespread Automation and Miniaturization
Automation has infiltrated almost all industries due to its efficiency and convenience for the end-user. Along with the domination of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in many applications and automation systems, the need for light and tiny devices has escalated even more. Rigid-flex will continue to be an important innovation in PCB assembly, especially for compact and seamless designs.
Green Technology
To combat the rising effects of climate change, electronics industries are now geared towards sustainable options, both in materials and processing. This is also tied with the government’s push to follow measures towards greener technologies. Rigid-flex board design and manufacturing also aim to comply with the standards and policies by seeking green materials and implementing energy-conservation systems.
Advanced Materials and Processing
The popularity of high-frequency and speed signals pushes the development of low-dielectric loss materials in PCB. Due to increasing complexity and miniaturization, new processing techniques and advanced materials are both important considerations in the future of the rigid PCB industry.
